
TO DO: IF NOT ALREADY IN YOUR FOLDER
CUT AND PASTE THE SOURCE CODE BELOW TO AN OPEN FILE WINDOW IN IDLE
AND SAVE IT AS
stickworks.py
"""
stickworks.py
Some infrastructure for working with Vectors and Edges, including
an xyplotter generator and axes maker.
By Kirby Urner, Sept 13, 2006
Updated Sept 29, 2006:
make Edge color a class-level attribute
add funky derivative demo
refactor a bit
Updated for Martian Math, 2010
Brought over Qvector subclass from coords.py
Code:
http://www.4dsolutions.net/ocn/python/stickworks.py
For colorized source:
http://www.4dsolutions.net/cgi-bin/py2html.cgi?script=/ocn/python/stickworks.py
Some relevant discussion:
http://mail.python.org/pipermail/edu-sig/2006-September/007145.html
http://mail.python.org/pipermail/edu-sig/2006-September/007149.html
http://mail.python.org/pipermail/edu-sig/2006-September/007150.html
http://mail.python.org/pipermail/edu-sig/2006-September/007312.html
"""
from visual import vector, cylinder, cross, dot, diff_angle, color
import visual
from operator import add, sub, mul, neg
root2 = 2.0**0.5
class Vector (object):
"""
A wrapper for visual.vector that expresses a cylinder via draw(),
always pegged to the origin
"""
radius = 0.03
def __init__(self, xyz, color=(0,0,1)):
self.v = vector(*xyz)
self.xyz = xyz
self.color = color
self.cyl = None
def draw(self):
"""define and render the cylinder"""
self.cyl = cylinder(pos = (0,0,0), axis = self.v, radius = self.radius, color = self.color)
def erase(self):
"""toss the cylinder"""
if self.cyl:
self.cyl.visible = 0
self.cyl = None
def __repr__(self):
return 'Vector @ (%s,%s,%s)' % self.xyz
# some vector ops, including scalar multiplication
def diff_angle(self, other):
return self.v.diff_angle(other.v)
def cross(self, other):
temp = cross(self.v, other.v)
return Vector((temp.x, temp.y, temp.z))
def dot(self, other):
return dot(self.v, other.v)
def __sub__(self, other):
temp = self.v - other.v
return Vector((temp.x, temp.y, temp.z))
def __add__(self, other):
temp = self.v + other.v
return Vector((temp.x, temp.y, temp.z))
def __mul__(self, scalar):
temp = self.v * scalar
return Vector((temp.x, temp.y, temp.z))
__rmul__ = __mul__
def __neg__(self):
return Vector((-self.v.x, -self.v.y, -self.v.z))
def _length(self):
return pow(self.v.x ** 2 + self.v.y ** 2 + self.v.z ** 2, 0.5)
length = property(_length)
def spherical(self):
"""Return (r,phi,theta) spherical coords based on current (x,y,z)"""
r = self.length()
if self.xyz[0]==0:
if self.xyz[1]==0: theta = 0.0
elif self.xyz[1]< 0: theta = 270.0
else: theta = 90.0
else:
theta = math.atan(self.xyz[1]/self.xyz[0]) * rad2deg
if self.xyz[0]<0 and self.xyz[1]==0: theta = 180
elif self.xyz[0]<0: theta = 180 + theta
elif self.xyz[0]>0 and self.xyz[1]<0: theta = 360 + theta
if r==0: phi=0.0
else: phi = math.acos(self.xyz[2]/r) * rad2deg
return (r,phi,theta)
def quadray(self):
"""return (a,b,c,d) quadray based on current (x,y,z)"""
x=self.xyz[0]
y=self.xyz[1]
z=self.xyz[2]
a = (2./root2) * ((x>=0)*x + (y>=0)*y + (z>=0)*z)
b = (2./root2) * ((x<0)*(-x) + (y<0)*(-y) + (z>=0)*z)
c = (2./root2) * ((x<0)*(-x) + (y>=0)*y + (z<0)*(-z))
d = (2./root2) * ((x>=0)*x + (y<0)*(-y) + (z<0)*(-z))
return self.norm((a,b,c,d))
def norm(self,plist):
"""Normalize such that 4-tuple all non-negative members."""
return tuple(map(sub,plist,[min(plist)]*4))
def norm0(self):
"""Normalize such that sum of 4-tuple members = 0"""
q = self.quadray()
return tuple(map(sub,q,[reduce(add,q)/4.0]*4))
class Qray(Vector):
"""Subclass of Vector that takes quadray coordinate args"""
def __init__(self, arg, color=(0,0,1),*flag):
"""Initialize a vector at an (a,b,c,d) tuple (= arg).
NOTE: in accompanying essay, xyz units = sphere diameter
i.e. Vector((1,0,0)).length() is 1 D, therefore quadray
inputs must be scaled by 1/2 to fit this context, i.e.
tetra edge defined by 2 basis quadrays = 1 D."""
if len(arg)==3: arg = Vector(arg).quadray() # if 3-tuple passed
self.coords = self.norm(arg)
a,b,c,d = self.coords
self.xyz = ((0.5/root2) * (a - b - c + d),
(0.5/root2) * (a - b + c - d),
(0.5/root2) * (a + b - c - d))
self.v = vector(self.xyz)
self.color = color
self.cyl = None
def __repr__(self):
return "Qvector " + str(self.coords)
def dot(self,v1):
"""Return the dot product of self with another vector.
return a scalar"""
scalar = 0
return 0.5*reduce(add,map(mul,self.norm0(),v1.norm0()))
def cross(self,v1):
"""Return the cross product of self with another vector.
return a Qvector"""
A=Qray((1,0,0,0))
B=Qray((0,1,0,0))
C=Qray((0,0,1,0))
D=Qray((0,0,0,1))
a1,b1,c1,d1 = v1.quadray()
a2,b2,c2,d2 = self.quadray()
k= (2.0**0.5)/4.0
thesum = (A*c1*d2 - A*d1*c2 - A*b1*d2 + A*b1*c2
+ A*b2*d1 - A*b2*c1 - B*c1*d2 + B*d1*c2
+ b1*C*d2 - b1*D*c2 - b2*C*d1 + b2*D*c1
+ a1*B*d2 - a1*B*c2 - a1*C*d2 + a1*D*c2
+ a1*b2*C - a1*b2*D - a2*B*d1 + a2*B*c1
+ a2*C*d1 - a2*D*c1 - a2*b1*C + a2*b1*D)
return k*thesum
def quadray(self):
return self.coords
class Edge (object):
"""
Edges are defined by two Vectors (above) and express as cylinder via draw().
"""
radius = 0.03
color = (1,0,0)
def __init__(self, v0, v1, color=None):
if not color==None:
self.color = color
self.v0 = v0
self.v1 = v1
self.cyl = None
def draw(self):
"""define and render the cylinder"""
temp = (self.v1 - self.v0).xyz
self.cyl = cylinder(pos = self.v0.xyz, axis = vector(*temp),
radius = self.radius, color = self.color)
def erase(self):
"""toss the cylinder"""
if self.cyl:
self.cyl.visible = 0
self.cyl = None
def __repr__(self):
return 'Edge from %s to %s' % (self.v0, self.v1)
def getedges(faces):
"""
Extract edges from the faces list.
"""
edges = set()
for f in faces:
pairs = zip(f , f[1:]+(f[0],))
for p in pairs:
edges.add(tuple(sorted(p)))
return list(edges)
def xyplotter(domain, f):
"""
domain should be an initialized generator, ready for next() triggering.
f is any function of x. Consecutive Vectors trace connected edges.
"""
x0 = domain.next()
y0 = f(x0)
while True:
x1 = domain.next()
y1 = f(x1)
e = Edge( Vector((x0, y0, 0)), Vector((x1, y1, 0)) )
e.draw()
yield None
x0, y0 = x1, y1
def axes(x=0,y=0,z=0):
"""
Draw some axes on the VPython canvas
"""
v0 = Vector((x,0,0))
v0.draw()
v0 = Vector((-x,0,0))
v0.draw()
v0 = Vector((0,y,0))
v0.draw()
v0 = Vector((0,-y,0))
v0.draw()
v0 = Vector((0,0,z))
v0.draw()
v0 = Vector((0,0,-z))
v0.draw()
def dgen(start, step):
"""
generic domain generator
"""
while True:
yield start
start += step
def testme():
"""
>>> from stickworks import testme
Visual 2005-01-08
>>> testme()
See:
http://www.4dsolutions.net/ocn/graphics/cosines.png
"""
from math import cos
def f(x): return cos(x)
d = dgen(-5, 0.1)
axes(-5,1,0)
graph = xyplotter(d, f)
for i in xrange(100):
graph.next()
def testmemore():
"""
See:
http://www.4dsolutions.net/ocn/graphics/pycalculus.png
"""
def snakeywakey(x):
"""
Polynomial with x-axis crossings at 3,2,-3,-7, with scaler
to keep y-values under control (from a plotting point of view)
"""
return 0.01 * (x-3)*(x-2)*(x+3)*(x+7)
def deriv(f, h=1e-5):
"""
Generic df(x)/dx approximator (discrete h)
"""
def funk(x):
return (f(x+h)-f(x))/h
return funk
d1 = dgen(-8, 0.1)
d2 = dgen(-8, 0.1)
d3 = dgen(-8, 0.1)
axes(-8,5,3)
deriv_snakeywakey = deriv(snakeywakey)
second_deriv = deriv(deriv_snakeywakey)
graph1 = xyplotter(d1, snakeywakey)
graph2 = xyplotter(d2, deriv_snakeywakey)
graph3 = xyplotter(d3, second_deriv)
Edge.color = (1,0,0) # make snakeywakey red
for i in xrange(130):
graph1.next()
Edge.color = (0,1,0) # make derivative green
for i in xrange(130):
graph2.next()
Edge.color = (0,1,1) # make 2nd derivative cyan
for i in xrange(130):
graph3.next()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# testme()
testmemore()
|
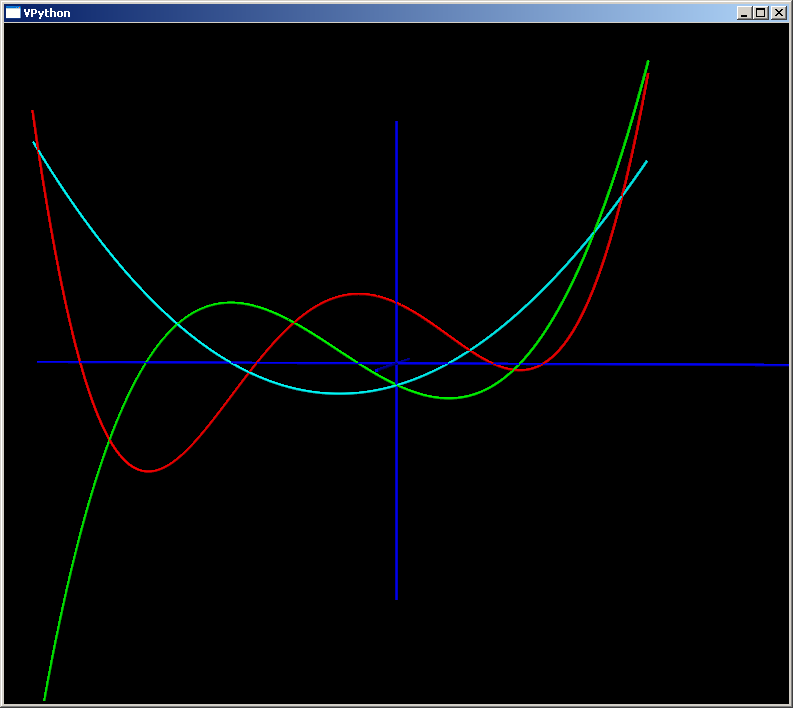
testmemore( )